How Many Open Heart Surgeries Can a Person Have
If y'all've had a middle assault, you may accept already had certain procedures to help you survive your heart set on and diagnose your condition. For example, many middle assault patients accept undergone thrombolysis, a procedure that involves injecting a clot-dissolving agent to restore claret flow in a coronary artery. This procedure is administered within a few (normally three) hours of a center attack. If this treatment isn't done immediately after a heart assault, many patients will need to undergo coronary angioplasty or coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG) later to meliorate claret supply to the heart muscle.
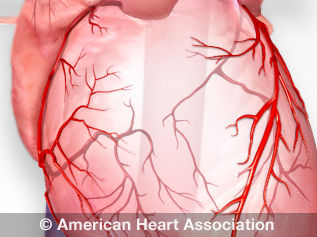
View an illustration of coronary arteries(link opens in new window).
See diagnostic tests and procedures to meliorate understand the tests you may have to undergo to find out if you had a eye assault, how much damage was washed and what degree of coronary artery disease (CAD) you accept.
Heart Procedures and Surgeries
Angioplasty
As well known as Percutaneous Coronary Interventions [PCI], Balloon Angioplasty and Coronary Artery Balloon Dilation.
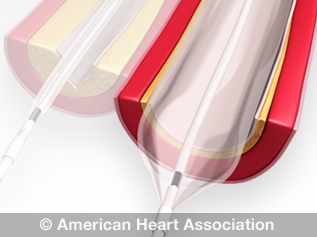
View an animation of angioplasty.
What the Procedure Does
Special tubing with an fastened deflated balloon is threaded upwardly to the coronary arteries. The airship is inflated to widen blocked areas where blood flow to the heart muscle has been reduced or cutoff. Oftentimes combined with implantation of a stent (see below) to help prop the avenue open up and decrease the hazard of another blockage. Considered less invasive considering the body is non cut open up. Lasts from 30 minutes to several hours. May require an overnight hospital stay.
Reason for the Procedure
- Greatly increases blood flow through the blocked artery.
- Decreases chest pain (angina).
- Increases ability for physical activity that has been express by angina or ischemia.
- Tin besides be used to open up cervix and brain arteries to help prevent stroke.
Medications That Your Doctor May Prescribe Mail-Procedure
Learn more almost cardiac medications, including dual antiplatelet therapy, that you may need to accept later on your procedure to forbid complications and to put you on the path for the best recovery.
Download our patient sheet: What is Coronary Angioplasty?
Angioplasty, Laser
What the Process Does
Similar to angioplasty except that the catheter has a laser tip that opens the blocked artery. Pulsating beams of light vaporize the plaque buildup.
Reason for the Procedure
- Increases blood flow through blocked arteries.
Bogus Centre Valve Surgery
(Also known equally Centre Valve Replacement Surgery)
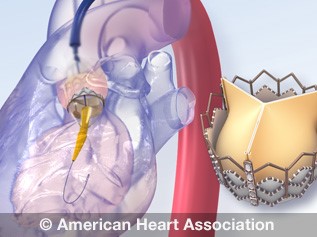
Sentry animations of heart valves and heart valve surgery options
What the Procedure Does
Replaces an aberrant or diseased heart valve with a good for you one.
Reason for the Procedure
- Restores part of the heart valves.
Download our patient canvass: What is Heart Valve Surgery?
Atherectomy
What the Procedure Does
Similar to angioplasty except that the catheter has a rotating shaver on its tip to cut abroad plaque from the artery.
Reason for the Process
- Increases blood catamenia through the blocked avenue past removing plaque buildup.
- May also be used in carotid arteries (major arteries of the neck leading to the encephalon) to remove plaque and reduce hazard for stroke.
Bypass Surgery
(Also known as CABG, pronounced "cabbage," Coronary Artery Bypass Graft done via Open up-Middle Surgery)
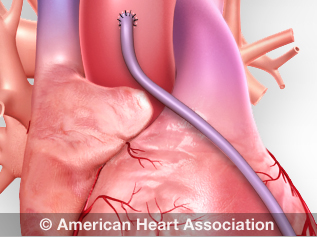
View an analogy of coronary bypass(link opens in new window).
What the Procedure Does
Treats blocked center arteries by taking arteries or veins from other parts of your body — called grafts — and using them to reroute the blood effectually the clogged avenue to supply blood flow to your eye muscle. View an animation of blood flow(link opens in new window). A patient may undergo one, two, three or more bypass grafts, depending on how many coronary arteries are narrowed. Requires several days in the hospital.
Download our patient sheet: What is Coronary Bypass Surgery?
Reason for the Procedure
- Ane of the well-nigh common and effective procedures to manage blockage of claret to the middle muscle.
- Improves the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart.
- Relieves chest pain (angina).
- Reduces risk of centre attack.
- Improves ability for physical activity that has been express by angina or ischemia.
Medications That Your Doctor May Prescribe Post-Process
Larn more near cardiac medications, including dual antiplatelet therapy, that you may demand to accept after your procedure to prevent complications and to put y'all on the path for the best recovery.
Cardiomyoplasty
What the Procedure Does
An experimental procedure in which skeletal muscles are taken from a patient's back or abdomen. And so they're wrapped around an ailing eye. This added muscle, aided by ongoing stimulation from a device similar to a pacemaker, may boost the heart's pumping motion.
Reason for the Procedure
- Increases the pumping motion of the heart.
Heart Transplant
What the Procedure Does
Removes a diseased heart and replaces it with a salubrious human eye when a heart is irreversibly damaged. Uses hearts from organ donation.
Reason for the Procedure
- Recognized as a proven procedure to restore heart health in appropriately selected patients.
Minimally Invasive Eye Surgery
(Also known every bit Limited Admission Coronary Artery Surgery and includes Port-Admission Coronary Avenue Featherbed (PACAB or PortCAB) and Minimally Invasive Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (MIDCAB or minimally invasive CABG)
What the Procedure Does
An alternative to standard featherbed surgery (CABG). Pocket-size incisions ("ports") are made in the chest. Chest arteries or veins from your leg are attached to the centre to "featherbed" the clogged coronary avenue or arteries. The instruments are passed through the ports to perform the bypasses. The surgeon views these operations on video monitors rather than directly. In PACAB, the middle is stopped and blood is pumped through an oxygenator or "centre-lung" machine. MIDCAB is used to avoid the center-lung machine. It's washed while the heart is still chirapsia. Requires several days in the hospital.
Reason for the Process
- Manages blockage of blood menstruum to the heart and improves the supply of blood and oxygen to the middle.
- Relieves breast pain (angina).
- Reduces risk of centre assault.
- Improves ability for physical activity.
Radiofrequency Ablation
(Too known as Catheter Ablation)
What the Procedure Does
A catheter with an electrode at its tip is guided through the veins to the heart muscle with real-time, moving X-rays (fluoroscopy) displayed on a video screen. The catheter is placed at the exact site within the heart where cells give off the electrical signals that stimulate the abnormal heart rhythm. And then a mild, painless radiofrequency energy (similar to microwave heat) is transmitted to the pathway. This destroys carefully selected heart musculus cells in a very pocket-size expanse (well-nigh 1/5 of an inch).
Reason for the Procedure
- Preferred treatment for many types of rapid heartbeats (arrhythmias) particularly supraventricular tachyarrhythmias.
Acquire more about Ablation.
Stent Placement
What the Procedure Does
A stent is a wire mesh tube used to prop open an artery during angioplasty. The stent stays in the artery permanently.

View an animation of a stent(link opens in new window).
Coronary narrowings tin can class again inside stents and are referred to as "restenosis."
Reason for the Procedure
- Holds the artery open.
- Improves blood flow to the middle muscle.
- Relieves chest pain (angina).
Download our patient sheet: What is a Stent? (PDF)
Medications That Your Physician May Prescribe Mail service-Procedure
Larn more about cardiac medications, including dual antiplatelet therapy, that y'all may need to take after your procedure to forestall complications and to put you on the path for the all-time recovery.
Transmyocardial Revascularization (TMR)
What the Procedure Does
An incision is made on the left breast to expose the heart. Then, a laser is used to drill a series of holes from the exterior of the middle into the heart's pumping chamber. In some patients TMR is combined with featherbed surgery. In those cases an incision through the breastbone is used for the bypass. Normally requires a hospital stay.
Reason for the Procedure
- Used to relieve severe chest pain (angina) in very sick patients who aren't candidates for bypass surgery or angioplasty.
Source: https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-attack/treatment-of-a-heart-attack/cardiac-procedures-and-surgeries
0 Response to "How Many Open Heart Surgeries Can a Person Have"
Post a Comment